GENERAL MEDICINE ASSINGMENT - MAY 2021
Yogita Ailani
Roll no: 149
31st MAY 2021
I have been given the following cases to solve in an attempt to understand the topic of "Patient clinical data analysis" to develop my competency in reading and comprehending clinical data including history, clinical findings, investigations, and diagnosis, and come up with a treatment plan.
The link given below contains questions asked regarding the cases:
http://medicinedepartment.blogspot.com/2021/05/online-blended-bimonthly-assignment.html?m=1
Below are my answers to the Medicine Assignment based on my comprehension of the cases.
- 1st episode of sob - 20 yr back
- 2nd episode of sob - 12 yr back
- From then she has been having yearly episodes from the past 12 yrs
- Diagnosed with diabetes - 8yrs back
- Anemia and took iron injections - 5yr ago
- Generalised weakness - 1 month back
- Diagnosed with hypertension - 20 days back
- Pedal edema - 15 days back
- Facial puffiness- 15 yrs back
- LUNGS - Bronchi and Bronchioles.
- This led to increased blood pressure in the pulmonary artery which resulted in RIGHT HEART FAILURE.
- Head end Elevation: Significantly increases global and regional end-expiratory lung volume. It has also been shown to improve oxygenation and hemodynamic performance.
- BiPAP Intermittent: By having a custom air pressure for when you inhale and a second custom air pressure when you exhale, the machine is able to provide relief to your overworked lungs and chest wall muscles.
- Chest physiotherapy: It is a term used for a group of treatments designed to improve respiratory efficiency, promote expansion of the lungs, strengthen respiratory muscles, and eliminate secretions from the respiratory system.It includes postural drainage, chest percussion, chest vibration, turning, deep breathing exercises, and coughing.
- Vitals Charting: This allow for continuous monitoring of a patient, with medical staff being continuously informed of the changes in general condition of a patient.
- Urine input/output chart: This chart (also known as a frequency-volume chart or bladder diary) is used to assess how much fluid you drink, to measure your urine volume, to record how often you pass urine over 24 hours and to show any episodes of incontinence (leakage).
- O2 Inhalation: It is used to
- manage the condition of hypoxia
- maintain o2 tension in blood plasma
- increase oxy haemoglobin in RBC
- maintain ability of cells to carry out normal metabolic function
- reduce the risk of complications.
- Hyponatremia:Worsening of HypoxiaRespiratory acidosisRight heart failure
- Hypochloremia:Respiratory acidosis with metabolic alkalosis
- Started drinking alcohol:2009 (12 years ago).
- Diagnosed with Diabetes Mellitus, prescribed oral hypoglycemic:2019 (2 years ago).
- Has an episode of seizures (most likely GTCS):2020 (1 year ago)
- Has another seizure episode (most likely GTCS)- following cessation of alcohol for 24 hours. Starts drinking again after seizure subsides:January 2021 (4months ago).
- Last alcohol intake, around 1 bottle. Starts having general body pains at night:Monday, May 10, 2021.
- Decreased food intake. Starts talking and laughing to himself. Unable to lift himself off the bed, help required:Tuesday, May 11, 2021.
- Conscious, but non coherent. Disoriented to time, person, place.Goes to an RMP the same day- is prescribed IV fluids and asked to visit a hospital
- Admitted to a tertiary care hospital for alcohol withdrawal symptoms, and is treated for the same:Saturday, May 15, 2021.
- As the urea levels are very high, it denotes an acute onset- Acute Renal Failure.
- As high serum creatinine, and urea levels are present, denotes that reabsorption from tubules is taking place- therefore the primary cause is prerenal, most probably due to generalised dehydration.
- A slightly high FENa level also denotes that tubular necrosis is occurring to some degree, hence the Prerenal AKI (mostly due to dehydration) is in turn leading to Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN).
- Alcohol causes iron deficiency by causing defect in cell production.
- Loss of blood through chronic foot ulcer
- Decreased bone marrow production of RBCs, due to EPO deficiency owing to kidney failure
- 13/5/2021 – Giddiness and vomiting (1 epidsode)
- 15/5/2021-Giddiness(increased),Bilateral hearing loss, aural fullness, tinnitus, Vomitings, Postural instability
4 days back- Patient consumed alcohol; He developed giddiness
H/O postural instability- falls while walking
Associated with bilateral hearing loss, aural fullness, presence of tinnitus
Associated vomiting- 2-3 episodes per day
Present day of admission- Slurring of speech, deviation of mouth that got resolved the same day
- August 2019 – Bipedal edema (pitting type)
- 12/5/2021 – pain in left arm
- 13/5/2021 – Chest pain
- 13/5/2021 – Difficulty in breathing (NYHA-CLASS-3)
- 13/5/2021 – Palpitations (more at night, increased since last night)
- Vertebral discs between C2, C3 and C4 vertebral bodies-in relation to Cervical spondylosis.
- Palpitations felt in chest
- Electrolyte imbalance (hypokalemia) causes manifestations like palpitations, chest heaviness, generalised body weakness.
- Radiating pain along her left upper limb due to cervical spondylosis.
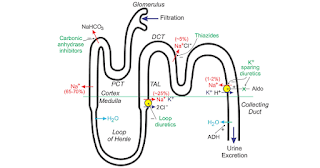
- Abnormal loses:Medications-diuretics, laxatives, enema, corticosteriodsReal causes- osmotic diuresis, mineralo corticoid excess, renal tubular acidosis, hypomagnesenemia.
- Trance cellular shift : alkalosis, thyrotoxicosis, delirium tremans, head injury, Myocardial, ischemia, recurrent hypokalemic periodic paralysis.
- Inadequate intake: anorexia, dementia, stareation, total parental nutrition
- Psuedohypokalemia:delayed sample analysis, significant leukocytosis
- Sudden loss of eye sight in one or both the eyes.
- Sudden headache without any known cause.
- Sudden dizziness, loss of balance and confusion.
- Sudden weakness or numbness in arms, legs and face especially on one side.
- Sudden trouble in walking, speaking and understanding speech.
Atrovas-Atorva 40 Tablet belongs to a group of medicines called statins. It is used to lower cholesterol and to reduce the risk of heart diseases. Cholesterol is a fatty substance that builds up in your blood vessels and causes narrowing, which may lead to a heart attack or stroke.
But since the patient is not a chronic alcoholic and so Alcohol might not have played any role.
- Degenerative cervical spondylosis
- Congenital stenosis
- Epidural abscess
- tumour
• Electrolyte imbalance(hypomagnesimia)• Iron deficiency anemia(mainly in endemic area of malaria)• hypogylcemia
Reduced ejection fraction: referred to as systolic heart failure.
- Chronic alcoholic - Since 40 years
- Diagnosed with type 2 DM - 30 years ago. Patient also diagnosed with diabetic triopahy indicating uncontrolled diabetes.
- Hypertension - 19 years ago.
- Elevated creatinine and AST/ASL ratio >2 and with chronic kidney disease IV
- Insulin resistance
- Prediabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Vascular complications, including retinopathy, nephropathy or neuropathy and related microvascular events.
- Diabetes mellitus-30 yrs
- Ckd-4 yrs
- Diabetic retinopathy-4 yrs
- Skin changes-bleps and diabetic ulcer-2 months
- Cardiac disorder-atrial fibrillation-diagnosed on ecg in hospital
- Shortness of breath - 2 days ago
- Decreased urine output - 2 days ago
- Anuria - since morning
The physical stress of hypertension on the arterial wall also results in the aggravation and acceleration of atherosclerosis, of the coronary and cerebral vessels. Hypertension appears to increase the susceptibility of the small and large arteries to atherosclerosis.
The cause of arterial thrombosis is artery damage due to atherosclerosis.
1. TAB. Dytor
Mechanism - Its action in antagonizing the effect of aldosterone, spironolactone inhibits the exchange of sodium for potassium in the distal renal tubule and helps to prevent potassium loss.
2. TAB. Acitrom
Mechanism - Acenocoumarol inhibits the action of an enzyme Vitamin K-epoxide reductase which is required for regeneration and maintaining levels of vitamin K required for blood clotting
3. TAB. Cardivas
Mechanism - Carvedilol works by blocking the action of certain natural substances in your body, such as epinephrine, on the heart and blood vessels. This effect lowers your heart rate, blood pressure, and strain on your heart. Carvedilol belongs to a class of drugs known as alpha and beta-blockers.
4. INJ. HAI
Mechanism - Regulates glucose metabolism
5.TAB. Digoxin
b) An enzyme that controls the movement of ions into the heart.
6. Hypoglycemia symptoms
7. Bleeding manifestations - Petechiae, Bleeding gums.
8. APTT and INR are ordered on a regular basis when a person is taking the anticoagulant drug warfarin to make sure that the drug is producing the desired effect.
- She developed sweating on exertion and shortness of breath even at rest – 13/05/2021
- SOB half an hour before coming to the hospital– 14/05/2021.
ANATOMICAL LOCATION: HEART
ETIOLOGY:
- Known c/o DM Type-2 since 12 years
- Known c/o Hypertension since 6 months
A)TAB MET XL 25 MG/STAT-contains Metoprolol as active ingredient
Indications - it is used to treat Angina, High blood pressure and to lower the risk of hear attacks .
INDICATIONS:
- Acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
- Non–ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS)
- Unstable angina.
- Stable angina.
- Anginal equivalent (e.g., dyspnea, arrhythmia, or dizziness or syncope).
- High risk stress test findings.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
- Intolerance for oral antiplatelets long-term.
- Absence of cardiac surgery backup.
- Hypercoagulable state.
- High-grade chronic kidney disease.
- Chronic total occlusion of SVG.
- An artery with a diameter of <1.5 mm.
COMPLICATIONS:
- Injury
to the heart arteries, including tears or rupture
- Infection,
bleeding, or bruising at the catheter site
- Allergic
reaction to the dye or contrast used
- Kidney
damage from the dye or contrast
- Blood
clots that can lead to stroke or heart attack
- Bleeding into the abdomen (retroperitoneal bleeding
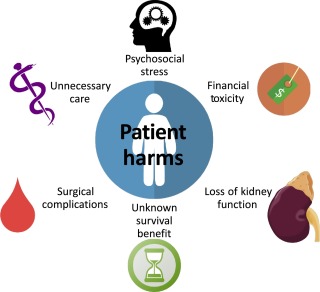
HARMS OF OVERTREATMENT AND OVERDIAGNOSIS:
The harms of over diagnosis and overtreatment are numerous Including psychosocial stressors, Renal morbidity, Unnecessary surgical complications.
- chest pain since 3 days from 11/o5/2021
- giddiness and profuse sweating on the day of admission – 14/05/2021
ANATOMICAL LOCATIONS: HEART coronary artery block rt coronary or left circumflex artery
§ ETIOLOGY: RISK FACTORS -hypertension and type 2 diabetes.
Mechanism - Aspirin inhibits platelet function through irreversible inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX) activity. Until recently, aspirin has been mainly used for primary and secondary prevention of arterial antithrombotic events.
2.TAB ATORVAS
Mechanism - Atorvastatin competitively inhibits 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase. By preventing the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, statin medications decrease cholesterol production in the liver.
3.TAB CLOPIBB
Mechanism - The active metabolite of clopidogrel selectively inhibits the binding of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) to its platelet P2Y12 receptor and the subsequent ADP- mediated activation of the glycoprotein GPIIb/IIIa complex, thereby inhibiting platelet aggregation. This action is irreversible.
4.INJ HAI
Mechanism - Regulates glucose metabolism
Insulin and its analogues lower blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake, especially by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production; insulin inhibits lipolysis and proteolysis and enhances protein synthesis; targets include skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue
Mechanism - Angioplasty, also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), is a minimally invasive endovascular procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclerosis.
PCI performed from 3 to 28 days after MI does not decrease the incidence of death, reinfarction or New York Heart Association (NYHA) class IV heart failure but it is associated with higher rates of both procedure-related and true ST elevation reinfarction.
there is decreased preload- so, SOB occurred due to decreased CO
IV fluids administered- there is increased preload- SOB decreased due to better of cardiac output.
EVOLUTION OF SYMPTOMS:
- Episode of fever and vomiting 5yrs back
- Pain abdomen (in umbilical, left hypochondriac, left lumbar and hypo gastric region) & vomiting since 1 week – 6/05/2021.
- Constipation, burning micturition, fever since 4 days – 9/05/2021.
ANATOMICAL LOCATION: Pancreas and Left lung
ETIOLOGY: Consumption of ALCOHOL
- Pancreatitis in its severe form is complicated by multiple organ system dysfunction, most importantly by pulmonary complications which include hypoxia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, atelectasis, and pleural effusion.
- The pathogenesis of some of the above complications is attributed to the production of noxious cytokines.
- Pulmonary complications of PANCREATITIS are divided into three stages.
- Stage 1-pulmonary manifestations without any radiological changes
- Stage 2-Showing radiologic changes
- Stage 3-ARDS.
- According to the above classification our patient falls in the 2nd stage as we have found PLEURAL EFFUSION on doing chest x-ray.
- Presence of pleural effusion is currently considered an indication of severe pancreatitis.it is characterized by high levels of amylase and protein. As we can see in our patient that his Serum Amylase levels are elevated.
- The pancreatic enzymes can track up into the mediastinum and then rupture into the pleural cavity either left side or bilaterally and so create a connection between the pancreatic duct and the pleural cavity. Pancreatic pleural effusions may be massive and require treatment.
- Treatment of pleural effusion is usually at first con-servative. Pleural effusions which become symptomatic often require thoracentesis, tube thoracotomy, endotracheal intubation, parenteral alimentation, and administration of octreotide. When the intraabdominal etiology is resolved, pleural effusions often resolve as well.
- LFT are increased due to hepatocyte injury.
- If the liver is damaged or not functioning properly, ALT can be released into the blood. This causes ALT levels to increase. A higher than normal result on this test can be a sign of liver damage
- Elevated alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), usually one to four times the upper limits of normal in alcoholic fatty liver.
- Specific marker for Alcoholic Fatty Liver disease - GGT (Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase)
Investigations:
✓ 24 hour urinary protein✓ Fasting and Post prandial Blood glucose
✓ HbA1c
✓ USG guided pleural tapping
Treatment:
• IVF: 125 mL/hr
• Inj PAN 40mg i.v OD
• Inj ZOFER 4mg i.v sos
• Inj Tramadol 1 amp in 100 mL NS, i.v sos
• Tab Dolo 650mg sos
• GRBS charting 6th hourly
• BP charting 8th hourly
- As alp and ast elevated
- Post operative complications like
- pyrexia (18.2%)
- nausea and vomiting (12%),
- wound infection (11.4%),
- respiratory tract infection (6.85%),
- urinary tract infection (2.28%)
- gastrointestinal complications (3.71%)
- toxemia and septicaemia (8%).
- Right lobe Atelectasis
- As we can see that patient falls under septic shock which causes low diastolic bp.
- NSAID-induced renal dysfunction has a wide spectrum of negative effects, including decreased glomerular perfusion, decreased glomerular filtration rate, and acute renal failure.
- Adverse effects - gastrointestinal mucosa injury.
- Difficulty in mictuation
- Electrolytic imbalance
- Infection
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, or excessive activity and impulsivity.
- For a diagnosis, the symptoms have to be present for more than six months
- Psychosomatic disorder
- Undiagnosed anxiety disorder
- If the cause is an overactive bladder, a medication known as an anticholinergic may be used. These prevent abnormal involuntary detrusor muscle contractions from occurring in the wall of the bladder
- To treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- For children 6 years of age and older, the recommendations include medication and behavior therapy together — parent training in behavior management for children up to age 12 and other types of behavior therapy and training for adolescents. Schools can be part of the treatment as well.
- Methylphenidate A stimulant and a medication used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. It can make you feel very ‘up’, awake, excited, alert and energised, but they can also make you feel agitated and aggressive. They may also stop you from feeling hungry.
- Amphetamine belongs to a class of drugs known as stimulants. It can help increase your ability to pay attention, stay focused on an activity, and control behavior problems. It may also help you to organize your tasks and improve listening skills.
- Cough - since 2 months on taking food and liquids
- Difficulty in swallowing since 2 month . It was initially difficult only with solids but then followed by liquids also.
- Laryngeal crepitus- positive
- These favour for tracheo esophageal fistula
- Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) represents the worsening of a recognized (paradoxical IRIS) or unrecognized (unmasking IRIS) pre-existing infection in the setting of improved immunologic function.
- The most effective prevention of IRIS would involve initiation of ART before the development of advanced immunosuppression. IRIS is uncommon in individuals who initiate antiretroviral treatment with a CD4+ T-cell count greater than 100 cells/uL.
- Cause of liver abscess in this patient is consumption of locally brewed toddy
- Yes , locally made alchohol acted as factor for liver abscess in this patient
- Liver abscess can be pyogenic ,amoebic or hydatid
- Infections are acquired from blood stream ( portal and systemic circulation)
- The most common pathophysiology is bowel content leakage and peritonitis . Bacteria travel via portal blood vessels into liver .
- In this case , Alcohol consumption specially locally prepared alchohol plays major role in liver abscess ( pyogenic and amoebic )
- Alchohol acts as predisposing factor
- Factors responsible for association between alcohol and liver abcess are as follows:
- Poor nutritional status due to alchohol consumption
- Presence of infective organisms in the locally prepared alcohol
- Immunity of the patient
- Damage to liver done by alchohol
- Yes ,liver abscess is more common in right lobe compared to left lobe
- Single lesions are more common in right lobe
- This is attributed to comparatively more blood supply via superior mesenteric vein on right side
- If the abcess is large ( 5cm or more) because it has more chances to rupture.
- If the abcess is present in left lobe as it may increase the chance of peritoneal leak and pericardial leak.
- If the abcess is not responding to the drugs for 7 or more days
- Pyogenic liver abscess
- polymicrobial
- Staphylococcus
- E .coli
- Klebsiella
- Streptococcus
- Amoebic liver abscess
- most commonly caused by Entamoeba hisolytica
- In this patient, occasional toddy consumption acted as source of pathogens
- Empirical antibiotics : cover both bacterial and amoebic causes
- For bacterial cause : penicillin +cephalosporin is given ( zostum 1.5 gm i.v. BD injection)
- For amoebic cause : metronidazole ( Metrogyl 500mg i.v. TID injection )
- Percutaneous drainage of abscess is not done in this patient because of the response to antibiotic therapy and associated complications of drainage
- Ultracet to relieve pain
- Dolo 650 mg for fever
- Age of patient – 21 yr ( young age ) , male gender
- Single abscess
- Right lobe involvement
- Chest x ray showing no involvement
- The abscess is more likely to be amoebic liver abscess
- Since we cannot take risk we treated patient for both bacterial and amoebic cause
- Detection of serum antibodies against Entamoeba
- Culture and sensitivity report of the aspirate
- Liposomal AmpB > Deoxycholate AmpB > Posaconazole
- Deoxycholate AmpB is cheaper compared to Liposomal AmpB















Comments
Post a Comment